返回
Compose动画学习之AnimationSpec 2022-11-30 by yaoxiawen
在compose动画的学习使用过程中,有一个参数属性一直存在,那就是AnimationSpec。不管是用于为单个值添加动画效果的animate*AsState,还是用于为多个值添加动画效果的updateTransition,亦或是一些封装好的高级别动画API:animatedContentSize、AnimatedVisibility,在这些里面都存在着AnimationSpec这个参数属性。但如果你并不了解并不会使用AnimationSpec,也不会阻碍你使用这些动画API,因为这些动画API都提供了默认的AnimationSpec实现。
1 2 3 4 5 interface AnimationSpec<T> { fun <V : AnimationVector> vectorize( converter: TwoWayConverter<T, V> ): VectorizedAnimationSpec<V> }
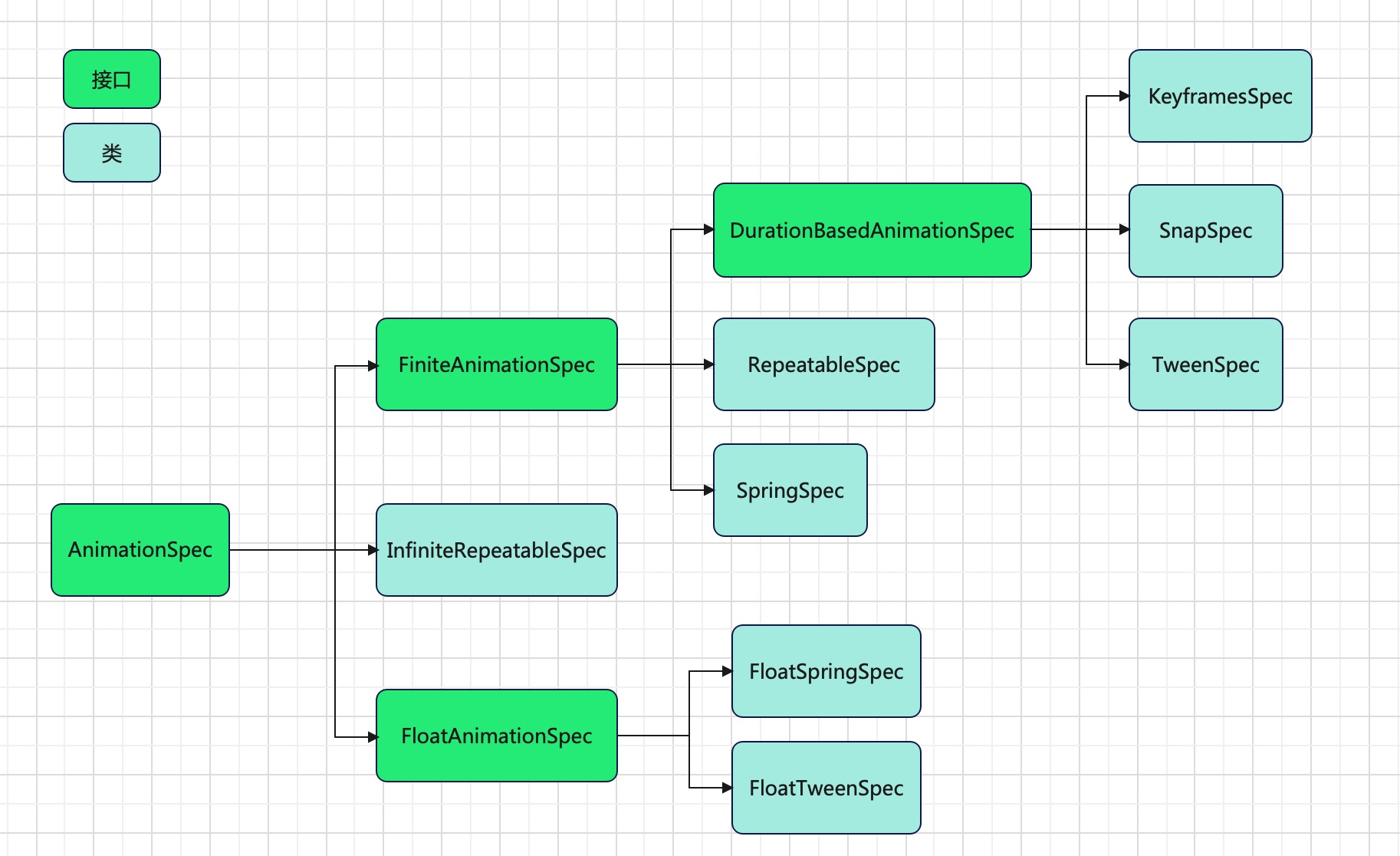
AnimationSpec,the specification of an animation,是一个接口,它用来存储动画规格,包括要进行动画处理的数据类型、将数据转换为动画后将使用的动画配置。
SpringSpec SpringSpec,弹性动画,是许多动画的默认AnimationSpec实现,例如animate*AsState、updateTransition、animatedContentSize等这些动画。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Stable fun <T> spring( dampingRatio: Float = Spring.DampingRatioNoBouncy, stiffness: Float = Spring.StiffnessMedium, visibilityThreshold: T? = null ): SpringSpec<T> = SpringSpec(dampingRatio, stiffness, visibilityThreshold)
官方提供了spring()方法用于构造SpringSpec,接收三个参数,但都有其默认值。
dampingRatio:阻尼比,默认值为Spring.DampingRatioNoBouncy = 1f,也就是没有弹性。当阻尼比<1时,阻尼比越低,弹簧越有弹性。
stiffness:刚度,默认值为Spring.StiffnessMedium。
visibilityThreshold:可见性阈值。
dampingRatio和stiffness都各有5个枚举值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Composable fun SpringDemo() { var small by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val size: Dp by animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (small) 40.dp else 100.dp, animationSpec = spring( dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioNoBouncy, stiffness = Spring.StiffnessHigh ) ) Column( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { small = !small }) { Text(text = "改变方块大小-spring") } Box( modifier = Modifier .size(size) .background(Color.LightGray) ) } }
我们使用一个size大小动画来观察SpringSpec效果,修改上述代码的spring中参数可以观察到各种SpringSpec效果,在同样的dampingRatio = Spring.DampingRatioNoBouncy,也就是没有弹性时,刚度越小,动画时间越长,动画效果越明显。而在较低的刚度下,阻尼比越小,弹性动画效果就越明显。
TweenSpec TweenSpec,用来创建使用给定的持续时间、延迟时间和缓和曲线配置的动画规格。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Stable fun <T> tween( durationMillis: Int = DefaultDurationMillis, delayMillis: Int = 0, easing: Easing = FastOutSlowInEasing ): TweenSpec<T> = TweenSpec(durationMillis, delayMillis, easing)
官方提供了tween()方法用于构造TweenSpec,接收三个参数,但都有其默认值。
durationMillis:动画持续时间,默认值为300毫秒。
delayMillis:动画延迟时间,默认值为0,也就是立即开始动画。
easing:动画曲线变化,默认值为FastOutSlowInEasing
1 2 3 4 @Stable fun interface Easing { fun transform(fraction: Float): Float }
Easing是一个接口,是一种调整动画分数的方法,允许过渡元素加速或减速,而不是以恒定的速度移动,Easing中有一个方法,方法中参数 fraction 是一个在0到1.0之间的值,表示动画中的当前进度点,其中0表示开始,1.0表示结束。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 //以静止开始和结束的元素使用此标准缓动。 他们快速加速并逐渐减速,以强调过渡的结束。这是最常见的方式。这相当于原生安卓插值器FastOutSlowInInterpolator val FastOutSlowInEasing: Easing = CubicBezierEasing(0.4f, 0.0f, 0.2f, 1.0f) //传入的元素使用减速缓动进行动画处理,它以峰值速度(元素运动的最快点)开始过渡并在静止时结束。这相当于原生安卓插值器LinearOutSlowInInterpolator val LinearOutSlowInEasing: Easing = CubicBezierEasing(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.2f, 1.0f) //退出屏幕的元素使用加速缓动,它们从静止开始并以峰值速度结束。这相当于原生安卓插值器FastOutLinearInInterpolator val FastOutLinearInEasing: Easing = CubicBezierEasing(0.4f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f) //线性、匀速缓动 val LinearEasing: Easing = Easing { fraction -> fraction }
我们将SpringSpec中的案例使用spring改为使用tween来观察TweenSpec效果,修改代码的tween中参数可以观察到各种TweenSpec效果。为了能更好的观察到动画效果,可以将动画时间适当设置长一点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Composable fun TweenDemo() { var small by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val size: Dp by animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (small) 40.dp else 100.dp, animationSpec = tween( durationMillis = 3000, easing = FastOutSlowInEasing ) ) Column( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { small = !small }) { Text(text = "改变方块大小-tween") } Box( modifier = Modifier .size(size) .background(Color.LightGray) ) } }
SnapSpec SnapSpec,描述了一种跳切类型的动画。 它立即将动画值捕捉到最终值。
1 2 @Stable fun <T> snap(delayMillis: Int = 0) = SnapSpec<T>(delayMillis)
官方提供了snap()方法用于构造SnapSpec,只有一个参数,delayMillis:动画延迟时间,默认值为0,也就是立即开始动画。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Immutable class SnapSpec<T>(val delay: Int = 0) : DurationBasedAnimationSpec<T> { override fun <V : AnimationVector> vectorize( converter: TwoWayConverter<T, V> ): VectorizedDurationBasedAnimationSpec<V> = VectorizedSnapSpec(delay) }
SnapSpec实现了DurationBasedAnimationSpec接口,还有上面已经介绍过的TweenSpec也是实现了DurationBasedAnimationSpec接口,此外还有KeyframesSpec。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Immutable class TweenSpec<T>( val durationMillis: Int = DefaultDurationMillis, val delay: Int = 0, val easing: Easing = FastOutSlowInEasing ) : DurationBasedAnimationSpec<T> { override fun <V : AnimationVector> vectorize(converter: TwoWayConverter<T, V>) = VectorizedTweenSpec<V>(durationMillis, delay, easing) }
1 2 3 4 interface DurationBasedAnimationSpec<T> : FiniteAnimationSpec<T> { override fun <V : AnimationVector> vectorize(converter: TwoWayConverter<T, V>): VectorizedDurationBasedAnimationSpec<V> }
DurationBasedAnimationSpec,描述了基于固定持续时间的 AnimationSpecs,例如 KeyframesSpec、TweenSpec 和 SnapSpec。 这些基于持续时间的AnimationSpec在放入RepeatableSpec时可以重复执行。
我们将上面的案例改为使用snap来观察SnapSpec效果,将动画延迟1秒来观察snap跳切的效果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Composable fun SnapDemo() { var small by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val size: Dp by animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (small) 40.dp else 100.dp, animationSpec = snap( delayMillis = 1000 ) ) Column( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { small = !small }) { Text(text = "改变方块大小-snap") } Box( modifier = Modifier .size(size) .background(Color.LightGray) ) } }
KeyframesSpec KeyframesSpec,基于动画持续时间中不同时间戳定义的值(即不同的关键帧)来制作动画。每个关键帧都可以使用KeyframesSpecConfig.at来进行定义。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Stable fun <T> keyframes( init: KeyframesSpec.KeyframesSpecConfig<T>.() -> Unit ): KeyframesSpec<T> { return KeyframesSpec(KeyframesSpec.KeyframesSpecConfig<T>().apply(init)) }
官方提供了keyframes()方法用于构造KeyframesSpec,只有一个参数KeyframesSpec.KeyframesSpecConfig。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class KeyframesSpecConfig<T> { //动画持续时间,默认为300 var durationMillis: Int = DefaultDurationMillis //动画延迟时间,默认为0 var delayMillis: Int = 0 //关键帧 internal val keyframes = mutableMapOf<Int, KeyframeEntity<T>>() //添加一个关键帧在某个时间点时刻 infix fun T.at(/*@IntRange(from = 0)*/ timeStamp: Int): KeyframeEntity<T> { return KeyframeEntity(this).also { keyframes[timeStamp] = it } } //添加一个关键帧在某个进度时刻 infix fun T.atFraction(fraction: Float): KeyframeEntity<T> { return at((durationMillis * fraction).roundToInt()) } //为刚提供的时间戳开始的时间间隔添加 Easing infix fun KeyframeEntity<T>.with(easing: Easing) { this.easing = easing }
KeyframesSpecConfig存储关键帧的可变配置,包括 durationMillis、delayMillis 和所有关键帧。 每个关键帧都定义了特定时间的动画值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @Composable fun KeyframesDemo() { var small by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val size: Dp by animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (small) 40.dp else 100.dp, animationSpec = keyframes { durationMillis = 1000 50.dp at 0 with LinearOutSlowInEasing 60.dp at 100 with FastOutLinearInEasing 70.dp at 300 80.dp at 600 } ) Column( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { small = !small }) { Text(text = "改变方块大小-keyframes") } Box( modifier = Modifier .size(size) .background(Color.LightGray) ) } }
RepeatableSpec RepeatableSpec,构建一个基于DurationBasedAnimationSpec的重复动画。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Stable fun <T> repeatable( iterations: Int, animation: DurationBasedAnimationSpec<T>, repeatMode: RepeatMode = RepeatMode.Restart, initialStartOffset: StartOffset = StartOffset(0) ): RepeatableSpec<T> = RepeatableSpec(iterations, animation, repeatMode, initialStartOffset)
官方提供了repeatable()方法用于构造RepeatableSpec,四个参数,需要至少传入两个参数。
iterations:重复次数,理论上应大于1,等于1表示不重复,也就没有必要使用RepeatableSpec。
animation:将被重复的AnimationSpec,必须是DurationBasedAnimationSpec,也就是可以使用KeyframesSpec 、SnapSpec 和TweenSpec。
repeatMode:重复模式
initialStartOffset:动画开始的偏移
RepeatMode有两种模式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 enum class RepeatMode { //将重新启动动画,并从开始值到结束值进行动画处理。 Restart, //将在动画重复时反转上一次迭代 Reverse }
在 RepeatMode.Reverse 模式下重复时,强烈建议迭代次数为奇数。否则,动画可能会在完成最后一次迭代时跳转到结束值。
initialStartOffset 可用于延迟动画的开始或将动画快进到给定的播放时间。 此起始偏移量不会重复,而动画中的延迟(如果有)将重复。 默认情况下,偏移量为 0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @kotlin.jvm.JvmInline value class StartOffset private constructor(internal val value: Long) { constructor(offsetMillis: Int, offsetType: StartOffsetType = StartOffsetType.Delay) : this( (offsetMillis * offsetType.value).toLong() ) val offsetMillis: Int get() = abs(this.value.toInt()) val offsetType: StartOffsetType get() = when (this.value > 0) { true -> StartOffsetType.FastForward false -> StartOffsetType.Delay } }
StartOffset存储一个offsetMillis时间和StartOffsetType类型,StartOffsetType类型有两类:StartOffsetType.Delay延迟动画的开始和StartOffsetType.FastForward快进动画到给定的播放时间,并立即开始播放。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @kotlin.jvm.JvmInline value class StartOffsetType private constructor(internal val value: Int) { companion object { //延迟动画的开始 val Delay = StartOffsetType(-1) //快进动画到给定的播放时间,并立即开始播放。 val FastForward = StartOffsetType(1) } }
使用repeatable,将animation设置为一个1秒的匀速变化的tween动画,重复3次,重复方式为反转重复,initialStartOffset设置为延迟500毫秒,StartOffsetType.FastForward。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @Composable fun RepeatableDemo() { var small by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val size: Dp by animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (small) 40.dp else 100.dp, animationSpec = repeatable( iterations = 3, animation = tween(durationMillis = 1000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse, initialStartOffset = StartOffset(500, StartOffsetType.FastForward) ) ) Column( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { small = !small }) { Text(text = "改变方块大小-repeatable") } Box( modifier = Modifier .size(size) .background(Color.LightGray) ) } }
整个动画效果:快进到500毫秒处,然后立即开始匀速动画,又500毫秒后开始反转动画。
InfiniteRepeatableSpec InfiniteRepeatableSpec,构建一个基于DurationBasedAnimationSpec的无限重复动画。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Stable fun <T> infiniteRepeatable( animation: DurationBasedAnimationSpec<T>, repeatMode: RepeatMode = RepeatMode.Restart, initialStartOffset: StartOffset = StartOffset(0) ): InfiniteRepeatableSpec<T> = InfiniteRepeatableSpec(animation, repeatMode, initialStartOffset)
官方提供了infiniteRepeatable()方法用于构造InfiniteRepeatableSpec,相比RepeatableSpec少了一个参数iterations,无限重复动画自然是不需要重复次数的,其余参数都一样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Composable fun InfiniteRepeatableDemo() { var small by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val size: Dp by animateDpAsState( targetValue = if (small) 40.dp else 100.dp, animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( animation = tween(durationMillis = 1000, easing = LinearEasing), repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse, initialStartOffset = StartOffset(500, StartOffsetType.FastForward) ) ) Column( modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(), horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally ) { Button(onClick = { small = !small }) { Text(text = "改变方块大小-infiniteRepeatable") } Box( modifier = Modifier .size(size) .background(Color.LightGray) ) } }
FloatAnimationSpec FloatAnimationSpec是一个接口,有两个实现类,FloatTweenSpec仅针对Float类型做TweenSpec动画,FloatSpringSpec仅针对Float类型做SpringSpec动画。官方没有提供可以直接进行使用的方法,因为tween()和spring()支持全量数据类型,FloatAnimationSpec是底层做更精细的计算的时候才会去使用。